Therapeutics
The other application of exosomes and more generally EVs pertains to their use as therapeutic agents, either for their inherent potential or as vehicle to the delivery of drug payloads or more recently miRNAs or SiRNAs (iExosomes).
The relatively (very) low immune clearance of exosomes, and their efficiency and good tolerability have been established on several mice studies. ‘Natural’ exosomes isolated from adult multipotent stem cells (Mesenchymal stem cells, MSC), have been tested to treat diseases ranging from stroke to Osteoarthritis, and pulmonary infection.
The confirmation that exosomal microRNAs effectively engage target mRNA and suppress gene expression in recipient cells has led to trials where the exosome content was enriched in a specific miRNA or small interfering RNA (siRNA). These modified exosomes carrying siRNA have been tested in several studies.
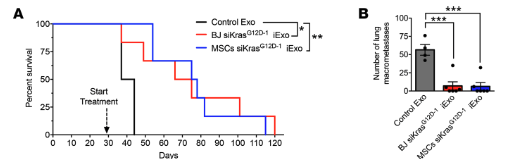
Example: Clinical grade MSC derived exosomes with KrasG12DSiRNA to treat pancreatic cancer (PDAC) in mice. [Ref: Mendt et Al, JCI insight, (2018), 99263, 3(8))]. Here, the iExosomes target oncogenic Kras to suppress patient derived xenograft:
Finally, exosomes have also been tested as actual drug delivery vehicles, to efficiently deliver drugs inside the target cells. For example, in Development of Exosome-encapsulated Paclitaxel to Overcome MDR in Cancer cells [Ref: Kim et Al, Nanomedicine (2016), 655-664, 12 (3)], macrophage exosomes were isolated and ‘loaded’ with Paclitaxel, a potent chemotherapeutic agent in a mouse model of multidrug resistant lung carcinoma metastases. The efficient delivery and the observed tissue of origin cell tropism.
Other modifications of exosomes have been demonstrated, for example, membrane modification to enhance cell type specific targeting, allowing for a tissue specific delivery or their payload (siRNA, other active principle). A very large number of clinical trials (>100) are ongoing involving the use of Exosomes for a range of applications.
This new field will require a stable, reliable method of EV isolation and preparation to pass the requirements of clinical trials testing. The conservative nature and the scalability of the NBI exosome isolation method makes it ideal to use as a therapeutic vehicle, since the vesicles are perfectly preserved, in contrast with other isolation methods (e.g., ultracentrifucation).
